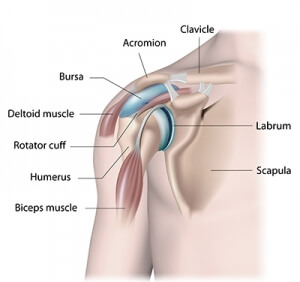
The shoulder is a “ball and socket” joint made up of three bones: the scapula (shoulder blade and socket), the clavicle (collarbone) and the humerus (upper arm bone). The head of the humerus rests in a shallow socket in the shoulder blade, called the glenoid. The glenoid is surrounded by the labrum—soft, meniscus-like tissue which deepens the socket and helps to hold the humeral head (“ball”) in place.
When the labrum is injured, the stability of the shoulder joint is compromised leaving it vulnerable to further dislocations, early arthritis, and gradual bone loss. Fortunately, with early intervention and specialized treatment, we are able to reduce the risk of repeated dislocations and preserve the long-term health of the joint.
Causes and Symptoms of Labral Tears
The most common cause of a shoulder labral tear is a shoulder dislocation. Repetitive activities or an acute injury—such as a fall or blow to the shoulder—can also cause damage to the labrum.
Common symptoms of labral tears include:
- Feeling of instability or looseness
- Recurrent shoulder dislocations
- Sharp, deep pain within the shoulder (especially with overhead activity and lifting)
- Decreased range of motion
- Decreased shoulder strength
Symptoms vary depending on the severity and location of the tear. To avoid irreparable joint damage, it’s important to visit your doctor if you experience any ongoing pain or weakness in the shoulder.
Types of Labral Tears
Anterior Labral Tear (Bankart Tear)
The most common type of shoulder ligament injury, an anterior tear (also called a Bankart lesion) is a tear of the labrum in the front of the shoulder. Especially common among younger athletes, Bankart tears often occur with a shoulder dislocation caused by a fall or twist of the arm. Larger tears can cause the shoulder joint to dislocate more easily over time.
Superior Labral Tear (SLAP Tear)
A SLAP tear, or SLAP lesion, occurs at the uppermost (superior) area of the labrum where the biceps tendon attaches to the labrum. Athletes involved in sports that require repetitive overhead arm motion are especially vulnerable to this type of tear as well as patients who lift repeatedly. These patients primarily feel a deep sharp shoulder pain during activity.
Posterior Labral Tear (Reverse Bankart Tear)
A posterior labral tear is a tear in the labrum located at the back of the shoulder. These tears are most common among athletes involved in weightlifting and other weight-bearing activities that put excess stress on the shoulder.
Degenerative Labral Tear
Degenerative labral tears are caused by wear-and-tear on the shoulder due to arthritis. These tears are distinctly different from the others as they don’t typically reduce function and, therefore, don’t require repair. Degenerative tears are often addressed at the time of a more advanced arthritis surgery, such as shoulder replacement. A shoulder specialist will be able to tell the difference between a degenerative labral tear that doesn’t require surgery and others that cause pain.
Labral Tear Diagnosis & Treatment:
The first step to determining the most effective treatment plan is an appropriate diagnosis. Your doctor will ask you about the history of the problem such as:
- How and when did it happen?
- How many times has it happened?
- What activities are difficult for you?
Following a history evaluation, a physical exam will be conducted including precise maneuvers to test each part of the irritated labrum.
If needed, advanced imaging techniques, such as an MRI, can provide a clear view to determine the extent of damage to the labrum and surrounding area.
 Does a torn labrum require surgery?
Does a torn labrum require surgery?
Not always. When determining the best treatment plan for a labral tear, there are multiple factors to consider such as:
- Size and type of tear
- Patient’s age and activity level
- Associated injuries or dislocations (past or present)
- Bone loss of the “ball” and “socket”
Physical therapy and home exercise programs can often be the first line of treatment for patients with less severe labral tears. Programs typically last 3-6 months and are specially designed to restore range-of-motion and strength to the shoulder. For patients involved in athletic activities, specific training and rehabilitation protocol can assist patients to returning to full activities.
While therapy can often alleviate symptoms caused by smaller tears, larger tears or tears associated with additional injuries may require surgery to reduce pain and restore stability.
With each dislocation, the shoulder becomes increasingly susceptible to future dislocation and instability which, in turn, puts the shoulder at risk of early onset arthritis and bone loss. By developing personalized algorithms, our specialized shoulder surgeons can help limit your risk of future problems.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Treatment for Labral Tears:
Labral repair
Using minimally invasive techniques, the damaged area is debrided (cleaned out), repaired, and reattached. Labral repair is typically performed arthroscopically on an outpatient basis.
Biceps tenodesis
Biceps tenodesis is a procedure in which the biceps tendon is detached from the superior labrum and reattached further down the humerus (arm bone). Biceps tenodesis can be performed to reduce tension on the labrum allowing it to heal. Patients will have no weakness in their biceps after this procedure.
How can we help?
Too often, patients are left unaware of options involving specialty surgeries outside of the surgeon’s “comfort-zone”. Our specialized surgeons are fellowship trained in a variety of surgical procedures, including minimally invasive/arthroscopic treatment, open reconstruction, and procedures involving bone loss. Our expertise allows us to provide our patients with a comprehensive, step-by-step pathway to improving their shoulder function.
While we focus on preserving the joint whenever possible using minimally-invasive methods, some patients can require a shoulder replacement to relieve their pain and improve their function. When needed, our fellowship-trained shoulder replacement specialists are available for consultation and will guide you through the process.